What Is Dark Energy? The mysterious Force Tearing the Universe Apart.
What Is Dark Energy? A Mysterious Force Tearing the Universe Apart.

Image Credit: NASA.
Imagine everything you’ve ever seen, the stars, the Sun, the planets, galaxies, all of it only accounts for less than 5% of the Universe. Then what is the else made of? It is dark energy. But what is dark energy? And what does it do? About 27% is dark matter, which holds galaxies together. But the rest, the dominant 68%, is something strange, completely invisible and even more powerful than gravity. It’s called Dark Energy.
When And How Was Dark Energy Discovered?
 |
| Image Credit: NASA. |
When And How Was Dark Energy Discovered?
After the Big Bang, around 13.8 billion years ago, the Universe started expanding. This expansion was slowing down and scientists thought that this was slowed down because of gravity which was natural. Then, in 1998, two independent teams of astrophysicists, The Supernova Cosmology Project and The High-Z Supernova Search Team made a shocking discovery. They observed distant Type Ia supernovae which is a massive exploding star used as “standard candles” to measure cosmic distances and found that the supernovae were fainter than expected which means that the galaxies were farther away than they should be.
But then, scientists found out that the Universe is not slowing down, instead, its speeding up. This meant that some unknown force which is opposite the gravity was pushing galaxies apart at an increasing speed. This unseen force became known as dark energy.
What Is It Exactly?
Scientists still don't know what exactly it is, but they know what it does:
- It exerts negative pressure which is the opposite of gravity.
- It appears to be evenly distributed in space.
- It does not clump like matter.
- It affects the geometry and fate of the Universe.
Is It Energy of Empty Space?
Einstein first proposed the idea of a cosmological constant (Λ) which is a constant energy density filling space to keep the Universe static. He later rejected it when the Universe was found to be expanding. But in the light of new evidence, scientists revived this idea that maybe space itself has an energy and even a perfect vacuum.
The Theories That Try to Explain It:
Dark energy is still unknown, but still there are theories that suggests much information about dark energy:
1. What Is the Theory of The Cosmological Constant (Λ)?
This theory suggests the following things:
- Suggests dark energy is a constant property of space itself.
- The more space expands, the darker energy exists because there's more space.
- This theory fits well with ΛCDM which is the standard cosmological model.
2. What Is Quintessence?
This theory suggests that:- Dark energy is not constant but a scalar field that changes over time and space.
- Dark energy behaves like a fluid with negative pressure.
- Dark energy could evolve with the Universe and even decay in the future.
3.What Is Phantom Energy?
This theory says that:
- Energy density increases as the Universe expands.
- Dark energy could lead to the Big Rip where galaxies, stars, atoms, and even space-time get torn apart.
How Do We Study Dark Energy?
Scientists can’t detect dark energy directly, but we can observe its influence on cosmic structures:
1.How Do we Study It Through Type Ia Supernovae?
These are standard candles to measure cosmic acceleration.
2. How Cosmic Microwave Background Helps Us in Its Study?
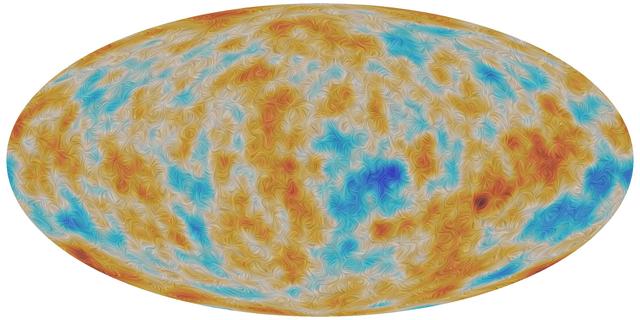
Image Credit: NASA. CMB (Cosmic Microwave Background).
It is a radiation from the early Universe. Precise measurements from missions like WMAP and Planck, it gives insights into how the Universe’s energy is distributed.
3. What Is Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO)?
These are ripples in the distribution of galaxies from the early Universe which act as cosmic rulers to track expansion.4.What is Gravitational Lensing?

Image Credit: NASA. Gravitational Lensing.
Light is bended around massive objects which reveals the distribution of dark energy and matter.
5.How Do Galaxy Clusters and Large-Scale Structure Helps Us in Studying Dark Energy?

Image Credit: NASA. Galaxy Cluster.
Studying how clusters form and evolve gives us clues about the influence of dark energy on cosmic growth.
What Is the Fate of the Universe According to Dark Energy?
Dark energy isn’t just a curiosity, but it decides the fate of the Universe.Depending on its nature, the Universe could end in the following ways:
1.What Is the Big Freeze / Heat Death?
If dark energy remains constant (Λ), galaxies will drift apart. Stars will burn out. The Universe will become a cold, dark and empty void.
2.What Is the Big Rip?
If dark energy becomes stronger over time, then this expansion will tear apart galaxies, stars, planets, atoms and even space-time itself.
3.What Is the Big Crunch / Rebirth?
If dark energy reverses or decays, gravity might eventually win, causing the Universe to collapse on itself, potentially followed by a new Big Bang.
4. The Multiverse Scenario:
Some theories suggest that dark energy’s value varies in other universes. We might live in a universe fine-tuned for life, among countless others with different physics.
Current Missions & the Future:
There are many missions launched to unravel the mystery behind dark energy:
Major Missions Studying the Dark Matter:
- Euclid Space Telescope (ESA, launched 2023).
- Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (NASA, upcoming).
- Dark Energy Survey (DES).
- Vera C. Rubin Observatory.
- DESI (Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument).
These missions aim to map billions of galaxies, measure expansion precisely, and decode the nature of dark energy across time.Why Should We Care?
Dark energy challenges everything we think we know:
- The laws of physics might be incomplete.
- It could lead to new particles, forces, or even dimensions.
- It forces us to redefine reality, space, time, and the fabric of existence.
Studying dark energy is about more than numbers. It’s about understanding our cosmic destiny and maybe one day, using that knowledge to travel through space in ways we can’t yet imagine.
Facts About Dark Energy:
- Dark energy makes up 68% of the Universe:
After the Big Bang, around 13.8 billion years ago, the Universe started expanding. This expansion was slowing down and scientists thought that this was slowed down because of gravity which was natural. Then, in 1998, two independent teams of astrophysicists, The Supernova Cosmology Project and The High-Z Supernova Search Team made a shocking discovery. They observed distant Type Ia supernovae which is a massive exploding star used as “standard candles” to measure cosmic distances and found that the supernovae were fainter than expected which means that the galaxies were farther away than they should be.
What Is It Exactly?
Scientists still don't know what exactly it is, but they know what it does:- It exerts negative pressure which is the opposite of gravity.
- It appears to be evenly distributed in space.
- It does not clump like matter.
- It affects the geometry and fate of the Universe.
Is It Energy of Empty Space?
Einstein first proposed the idea of a cosmological constant (Λ) which is a constant energy density filling space to keep the Universe static. He later rejected it when the Universe was found to be expanding. But in the light of new evidence, scientists revived this idea that maybe space itself has an energy and even a perfect vacuum.The Theories That Try to Explain It:
Dark energy is still unknown, but still there are theories that suggests much information about dark energy:1. What Is the Theory of The Cosmological Constant (Λ)?
This theory suggests the following things:- Suggests dark energy is a constant property of space itself.
- The more space expands, the darker energy exists because there's more space.
- This theory fits well with ΛCDM which is the standard cosmological model.
2. What Is Quintessence?
This theory suggests that:- Dark energy is not constant but a scalar field that changes over time and space.
- Dark energy behaves like a fluid with negative pressure.
- Dark energy could evolve with the Universe and even decay in the future.
3.What Is Phantom Energy?
This theory says that:- Energy density increases as the Universe expands.
- Dark energy could lead to the Big Rip where galaxies, stars, atoms, and even space-time get torn apart.
How Do We Study Dark Energy?
Scientists can’t detect dark energy directly, but we can observe its influence on cosmic structures:1.How Do we Study It Through Type Ia Supernovae?
2. How Cosmic Microwave Background Helps Us in Its Study?
 |
| Image Credit: NASA. CMB (Cosmic Microwave Background). |
3. What Is Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO)?
These are ripples in the distribution of galaxies from the early Universe which act as cosmic rulers to track expansion.
4.What is Gravitational Lensing?
 |
| Image Credit: NASA. Gravitational Lensing. |
Light is bended around massive objects which reveals the distribution of dark energy and matter.
5.How Do Galaxy Clusters and Large-Scale Structure Helps Us in Studying Dark Energy?
 |
| Image Credit: NASA. Galaxy Cluster. |
What Is the Fate of the Universe According to Dark Energy?
Dark energy isn’t just a curiosity, but it decides the fate of the Universe.
Depending on its nature, the Universe could end in the following ways:1.What Is the Big Freeze / Heat Death?
2.What Is the Big Rip?
3.What Is the Big Crunch / Rebirth?
4. The Multiverse Scenario:
Current Missions & the Future:
There are many missions launched to unravel the mystery behind dark energy:Major Missions Studying the Dark Matter:
- Euclid Space Telescope (ESA, launched 2023).
- Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (NASA, upcoming).
- Dark Energy Survey (DES).
- Vera C. Rubin Observatory.
- DESI (Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument).
Why Should We Care?
Dark energy challenges everything we think we know:- The laws of physics might be incomplete.
- It could lead to new particles, forces, or even dimensions.
- It forces us to redefine reality, space, time, and the fabric of existence.
Facts About Dark Energy:
- Dark energy makes up 68% of the Universe:
That’s more than all-stars, galaxies, black holes, and dark matter combined.
- It’s completely invisible:
You can’t touch it, see it, or detect it directly but only its effects.- It causes the Universe to expand faster and faster:
Like putting a cosmic foot on the gas pedal.
Scientists were measuring how fast the Universe was slowing down. Surprise: it wasn’t!
- It was discovered accidentally in 1998:
Scientists were measuring how fast the Universe was slowing down. Surprise: it wasn’t!- It overpowers gravity on large scales:
While gravity pulls things together, dark energy pushes them apart.
- It fills all of space, evenly:
Unlike matter or dark matter, which clumps into galaxies.
- Type Ia supernovae led to its discovery:
Distant exploding stars appeared dimmer than expected, they were farther away.
- It affects the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB):
Slight temperature fluctuations in the CMB help measure dark energy’s impact on early expansion.
- It’s being studied using galaxy maps and cosmic ripples:
Projects like Euclid, DESI, and the Roman Space Telescope are mapping billions of galaxies to track it.
- Gravitational lensing also reveals its presence:
By bending light, we can see how dark energy shape's cosmic structure.
Theoretical Facts:
- Einstein predicted something like it in 1917:
He called it the “cosmological constant” (Λ) but thought it was a mistake.- Dark energy has negative pressure:
This is what allows it to accelerate the expansion of the Universe.
- It might be a "scalar field" like quintessence:
This means it could change over time and maybe even disappear one day.- It could be a property of space itself:
The more space you have, the darker energy you get. Infinite loop?- Or gravity itself could be wrong:
Some physicists think dark energy is just a sign that Einstein’s theory needs tweaking on large scales.- There’s a vacuum energy discrepancy of 10¹²⁰:
Quantum theory predicts a much larger vacuum energy than we observe the biggest mismatch in physics.Mind Blowing Facts:
- Dark energy is not the same as dark matter:
Dark matter holds galaxies together; dark energy pushes them apart.
- It might be why life exists:
If dark energy were much stronger, matter wouldn't have formed. Too weak and the Universe would have collapsed early.- It was weaker in the early Universe:
Back then, matter and radiation dominated. Now, dark energy is winning.- Every second, space is being created:
And dark energy fills it instantly, everywhere.- You’re sitting in a sea of dark energy right now:
It’s in every cubic centimeter of your room, silently expanding space.- It will stretch space forever... unless it doesn’t:
We still don’t know if it’s constant or changing.- It may connect to the Multiverse:
Some theories suggest different universes have different dark energy values.- Its discovery won the Nobel Prize in 2011:
Saul Perlmutter, Brian P. Schmidt, and Adam G. Riess shared the award.- It could help unite quantum mechanics and gravity:
If we can understand it, it might unlock the long-sought “Theory of Everything.”
Conclusion:
Dark energy is not just a mystery, but it is the mystery of our time. It reminds us that the Universe still has secrets.

Comments
Post a Comment